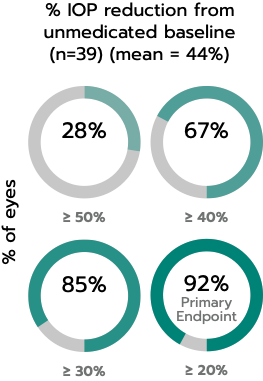
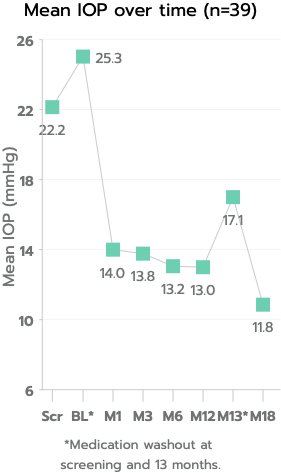
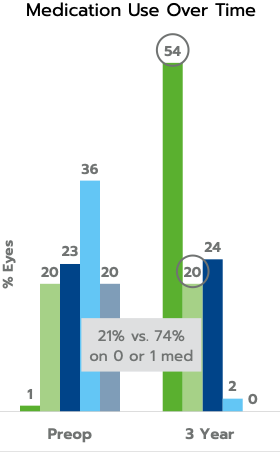
iStent inject® W Important Safety Information
Indications for Use
The iStent inject® W is intended to reduce intraocular pressure safely and effectively in patients diagnosed with primary open-angle glaucoma, pseudo-exfoliative glaucoma or pigmentary glaucoma. The iStent inject® W, can deliver two (2) stents on a single pass, through a single incision. The implant is designed to stent open a passage through the trabecular meshwork to allow for an increase in the facility of outflow and a subsequent reduction in intraocular pressure.
The device is safe and effective when implanted in combination with cataract surgery in those subjects who require intraocular pressure reduction and/or would benefit from glaucoma medication reduction. The device may also be implanted in patients who continue to have elevated intraocular pressure despite prior treatment with glaucoma medications and conventional glaucoma surgery.
Contraindications
The iStent inject® W System is contraindicated under the following circumstances or conditions:
- In eyes with primary angle closure glaucoma, or secondary angle-closure glaucoma, including neovascular glaucoma, because the device would not be expected to work in such situations.
- In patients with retrobulbar tumor, thyroid eye disease, Sturge-Weber Syndrome or any other type of condition that may cause elevated episcleral venous pressure.
Warnings/Precautions
- For prescription use only.
- This device has not been studied in patients with uveitic glaucoma.
- Do not use the device if the Tyvek® lid has been opened or the packaging appears damaged. In such cases, the sterility of the device may be compromised.
- Due to the sharpness of certain injector components (i.e. the insertion sleeve and trocar), care should be exercised to grasp the injector body. Dispose of device in a sharps container.
- iStent inject® W is MR-Conditional; see MRI Information here.
- Physician training is required prior to use of the iStent inject® W System.
- Do not re-use the stent(s) or injector, as this may result in infection and/or intraocular inflammation, as well as occurrence of potential postoperative adverse events as shown below under “Potential Complications.”
- There are no known compatibility issues with the iStent inject® W and other intraoperative devices (e.g., viscoelastics) or glaucoma medications.
- Unused product & packaging may be disposed of in accordance with facility procedures. Implanted medical devices and contaminated products must be disposed of as medical waste.
- The surgeon should monitor the patient postoperatively for proper maintenance of intraocular pressure. If intraocular pressure is not adequately maintained after surgery, the surgeon should consider an appropriate treatment regimen to reduce intraocular pressure.
- Patients should be informed that placement of the stents, without concomitant cataract surgery in phakic patients, can enhance the formation or progression of cataract.
Adverse Events
Please refer to Directions For Use for additional adverse event information.
Caution
Please reference the Directions For Use labelling for a complete list of contraindications, warnings and adverse events.