Three prospective, randomized, sham-controlled US phase III pivotal trials were conducted to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of Photrexa® Viscous (riboflavin 5’-phosphate in 20% dextran ophthalmic solution), Photrexa® (riboflavin 5’-phosphate ophthalmic solution), and the KXL system for performing the iLink® corneal cross-linking procedure in support of the FDA NDA submission.
Clinical Data
Clinical Data for iLink®
US Phase III Clinical Trial
Data Primary Efficacy Endpoint
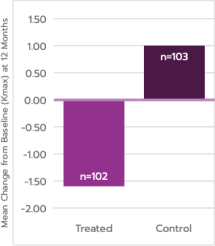
Progressive
Keratoconus
Mean Difference in
Kmax = 2.6 D
Meets definition of success,
p<0.0001

Corneal
Ectasia
Mean Difference in Kmax = 1.4 D
Meets definition of success,
p<0.0001
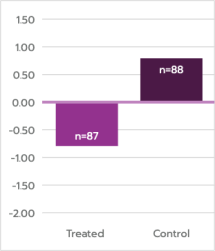

Primary endpoint met: ≥1 D difference in 12-month mean Kmax, treatment vs. control
*Post-baseline missing data were imputed using last available Kmax value. For the sham study eyes that received cross-linking treatment after baseline, the last Kmax measurement recorded prior to receiving cross-linking treatment was used in the analysis for later time points.
*Post-baseline missing data were imputed using last available Kmax value. For the sham study eyes that received cross-linking treatment after baseline, the last Kmax measurement recorded prior to receiving cross-linking treatment was used in the analysis for later time points.
US Phase III Clinical Trial Data:
Other Observed Findings
- In the pooled analysis of keratoconus patients, 94% of iLink® treated eyes showed improvement or remained within 2.00 D of baseline Kmax at 12 months [1].
- In the pooled analysis of corneal ectasia patients, 97% of iLink® treated eyes showed improvement or remained within 2.00 D of baseline Kmax at 12 months [2].
Safety
The majority of adverse events reported resolved during the first month. In 1-2% of patients, AEs continued to be reported at 12 months, including corneal epithelium defect, corneal edema, corneal opacity (haze) and corneal scar.
- In keratoconus patients, the most common ocular adverse reactions in CXL-treated eyes were corneal opacity (haze), punctate keratitis, corneal striae, corneal epithelium defect, eye pain, reduced visual acuity, and blurred vision.
- In corneal ectasia patients, the most common ocular adverse reactions were corneal opacity (haze), corneal epithelium defect, corneal striae, dry eye, eye pain, punctate keratitis, photophobia, reduced visual acuity, and blurred vision.
Citation:
- Hersh PS, Stulting RD, Muller D, Durrie DS, Rajpal RK; United States Crosslinking Study Group. United States Multicenter Clinical Trial of Corneal Collagen Crosslinking for Keratoconus Treatment. Ophthalmology. 2017 Sep;124(9):1259-1270.
- Hersh PS, Stulting RD, Muller D, Durrie DS, Rajpal RK; U.S. Crosslinking Study Group. U.S. Multicenter Clinical Trial of Corneal Collagen Crosslinking for Treatment of Corneal Ectasia after Refractive Surgery. Ophthalmology. 2017 Oct;124(10):1475-1484.

