Micro Stents. Macro Efficacy.
iStent inject® W builds on the trabecular micro-bypass technology of iStent inject®, which has demonstrated efficacy across a wide range of clinical studies.
Clinical Data

iStent inject® W builds on the trabecular micro-bypass technology of iStent inject®, which has demonstrated efficacy across a wide range of clinical studies.
US Pivotal Trial at 24 Months1
≥ 20% Reduction in Unmedicated DIOP
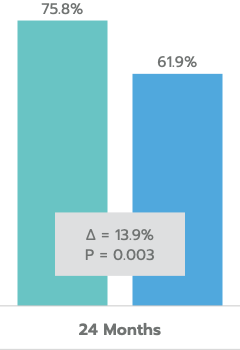
Mean Unmedicated DIOP Reduction
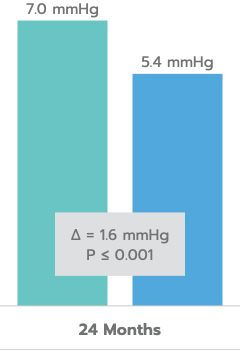
In the US IDE Trial (n=505 subjects), iStent inject® met all study endpoints and demonstrated a clinically significant reduction in IOP for iStent inject® subjects at 24 months.
Other Observed Data:
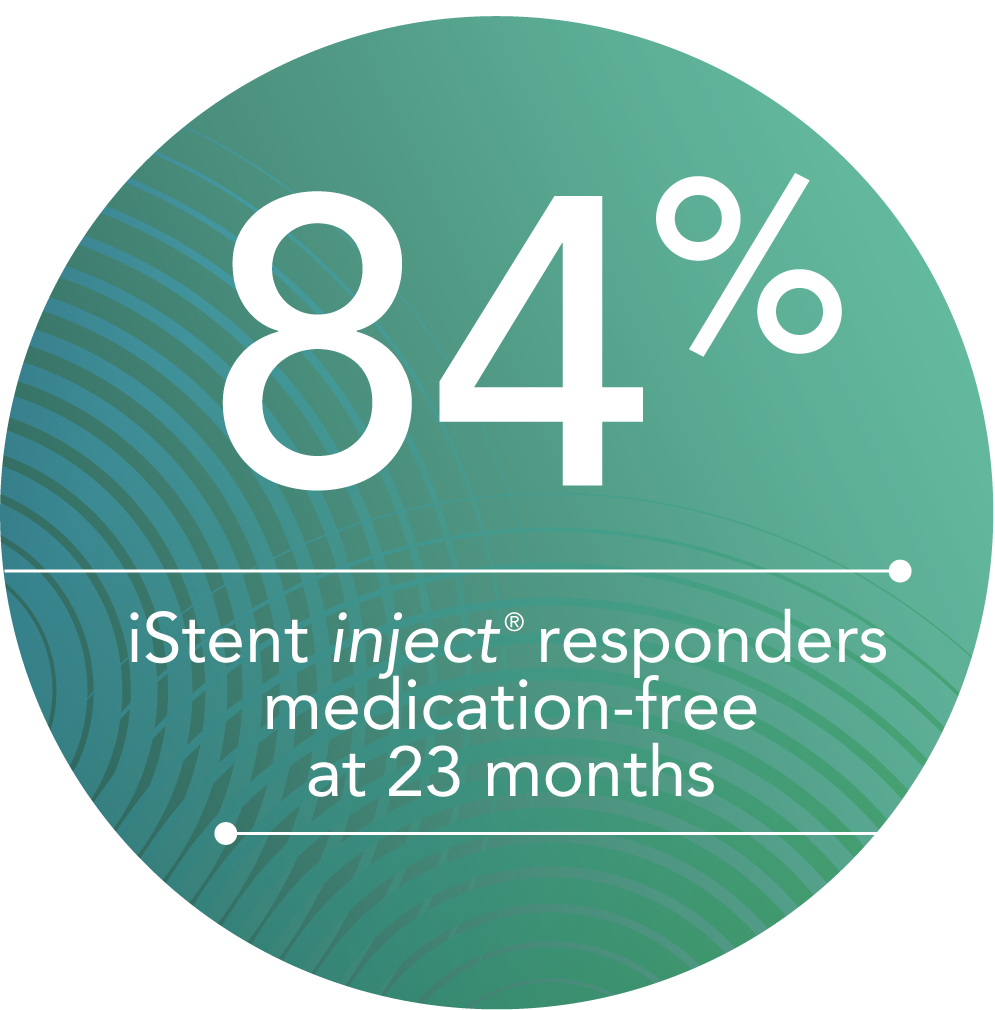
Additional independent, long-term studies of Glaukos trabecular micro-bypass technology suggest that results are maintained several years after the procedure.
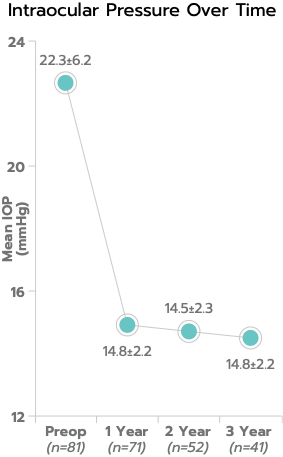
In a consecutive case series with three-year follow-up, mean IOP was 14.3 ± 1.7 mm Hg, representing a 37% reduction from preoperative medicated mean IOP of 22.6 ± 6.2 mm Hg; and 100% of eyes had IOP ≤ 18 mm Hg.
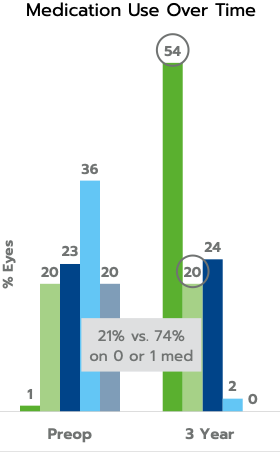
In the same consecutive case series, mean medication use was decreased from 2.5 to 0.8 medications at three years, a 68% reduction; and 74% of eyes were using 0 or 1 medication compared to 21% preoperatively.
In the US IDE pivotal study, iStent inject® had no reports of hypotony, significant hyphema, flat anterior chamber, choroidal hemorrhage or effusion, or myopic shift.1,6
Medication reduction is subject to the discretion of the physician.
Five posters presented at ARVO 2021 highlight the efficacy and safety of the iStent platform as compared to other procedures.
The iStent inject® W Trabecular Micro-Bypass System Model G2-W is indicated for use in conjunction with cataract surgery for the reduction of intraocular pressure (IOP) in adult patients with mild to moderate primary open-angle glaucoma.
The iStent inject® W is contraindicated in eyes with angle-closure glaucoma, traumatic, malignant, uveitic, or neovascular glaucoma, discernible congenital anomalies of the anterior chamber (AC) angle, retrobulbar tumor, thyroid eye disease, or Sturge-Weber Syndrome or any other type of condition that may cause elevated episcleral venous pressure.
Gonioscopy should be performed prior to surgery to exclude congenital anomalies of the angle, PAS, rubeosis, or conditions that would prohibit adequate visualization of the angle that could lead to improper placement of the stent and pose a hazard.
The iStent inject® W is MR-Conditional, i.e., the device is safe for use in a specified MR environment under specified conditions; please see Directions for Use (DFU) label for details.
The surgeon should monitor the patient postoperatively for proper maintenance of IOP. The safety and effectiveness of the iStent inject® W have not been established as an alternative to the primary treatment of glaucoma with medications, in children, in eyes with significant prior trauma, abnormal anterior segment, chronic inflammation, prior glaucoma surgery (except SLT performed > 90 days preoperative), glaucoma associated with vascular disorders, pseudoexfoliative, pigmentary or other secondary open-angle glaucomas, pseudophakic eyes, phakic eyes without concomitant cataract surgery or with complicated cataract surgery, eyes with medicated IOP > 24 mmHg or unmedicated IOP < 21 mmHg or > 36 mmHg, or for implantation of more or less than two stents.
Common postoperative adverse events reported in the iStent inject® randomized pivotal trial included stent obstruction (6.2%), intraocular inflammation (5.7% for iStent inject® vs. 4.2% for cataract surgery only), secondary surgical intervention (5.4% vs. 5.0%) and BCVA loss ≥ 2 lines ≥ 3 months (2.6% vs. 4.2%).
Federal law restricts this device to sale by, or on the order of, a physician. Please see DFU for a complete list of contraindications, warnings, precautions, and adverse events.